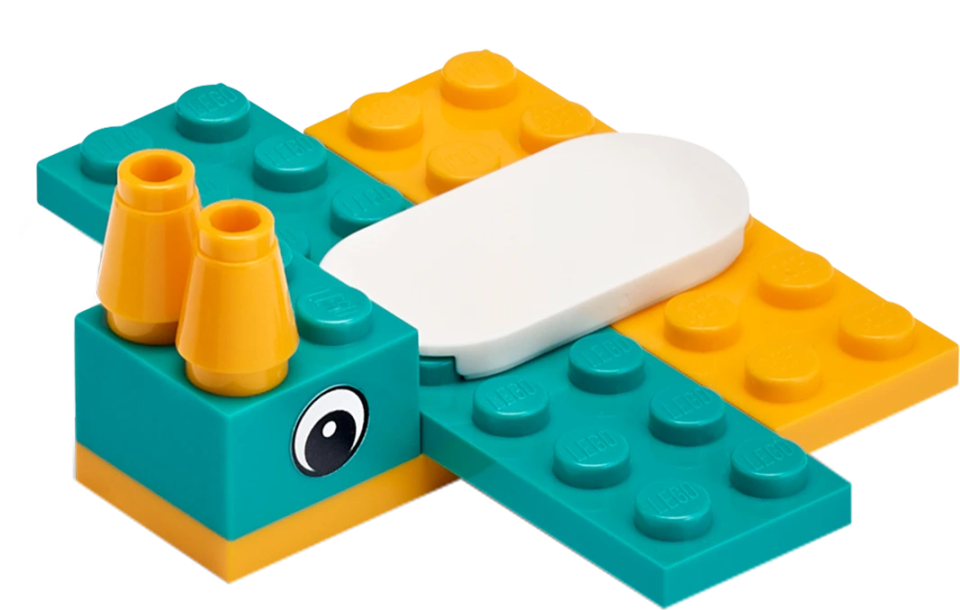
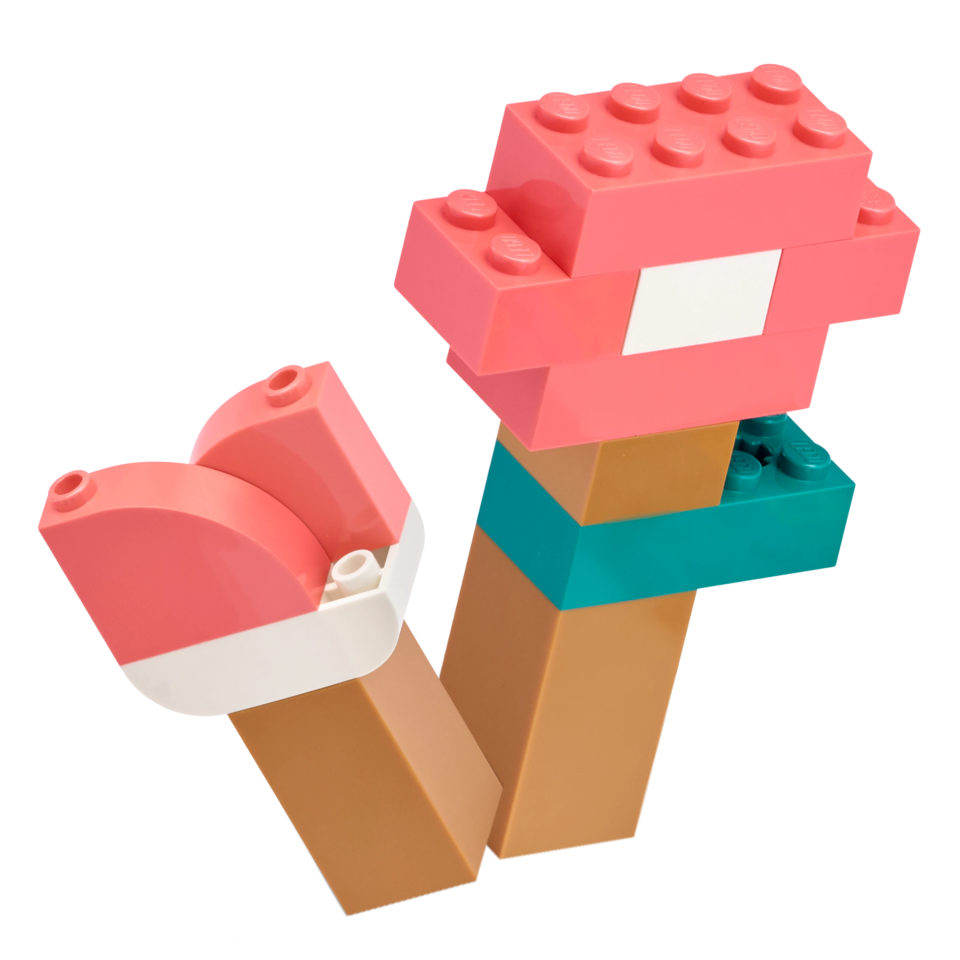
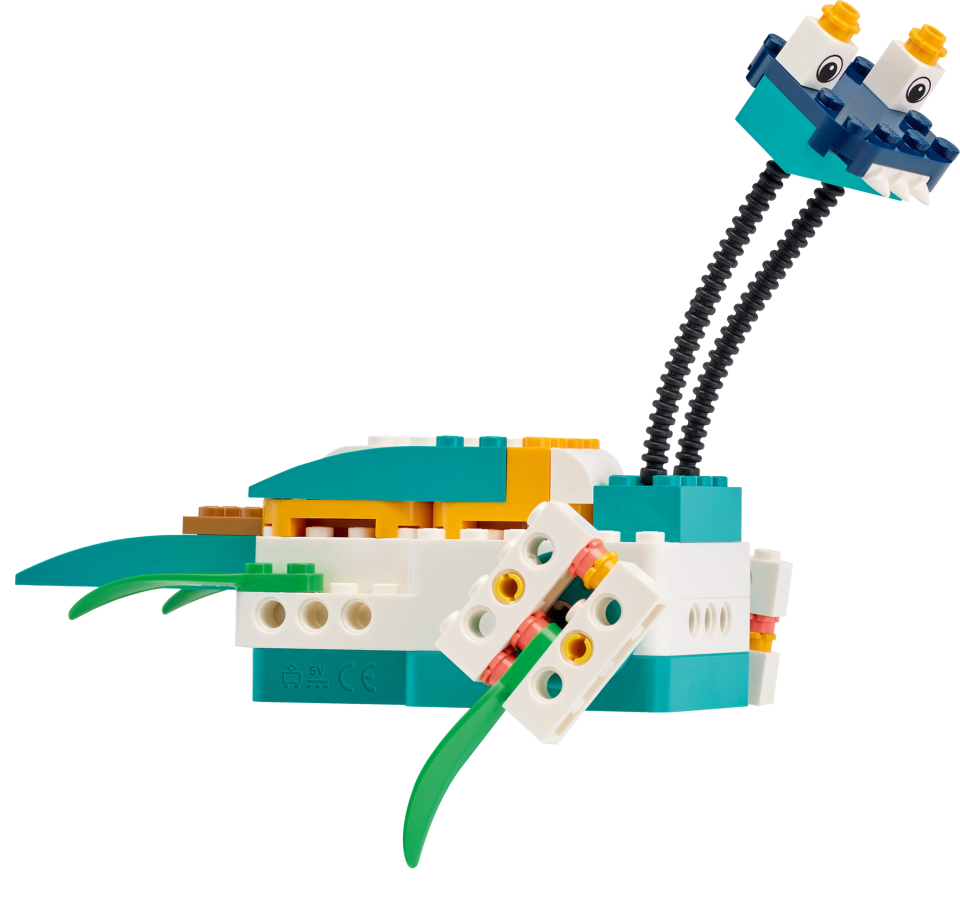
Objects and Obstacles
Use the Ultrasonic Sensor to detect and react to the Cuboid.

Lesson plan
1. Prepare
- Read through the pupil material in the EV3 Classroom App.
- Collect information about how the Ultrasonic Sensor works.
- You’ll need a tape measure to measure out where to place the Cuboid in this lesson.
- In order to complete this lesson, the pupils will have to have built the Driving Base model, which will take about 30 minutes to complete.
2. Engage (5 Min.)
- Use the ideas in the ‘Ignite a Discussion’ section below to engage your pupils in a discussion relating to this lesson.
- Divide your class into teams of two pupils.
3. Explore (20 Min.)
- Have each team build the Cuboid, and the Ultrasonic Sensor extension for their Driving Base.
- Allow the pupils time to use the provided programming stacks to explore ways in which the Ultrasonic Sensor can be used.
4. Explain (5 Min.)
- Facilitate a discussion about how the Ultrasonic Sensor could be used to measure distance.
5. Elaborate (15 Min.)
- Challenge your pupils to program their Driving Bases to beep faster or louder as they get closer to the Cuboid.
- Don’t forget to leave some time for tidying up.
6. Evaluate
- Give feedback on each pupil’s performance.
- To simplify the process, you can use the assessment rubrics that have been provided.
Ignite a Discussion
Modular robots are useful because they can be extended and reconfigured to perform a wide range of tasks. Adding sensors enables them to react to their environment so that they can do things like detect obstacles and avoid collisions.

Use these questions to engage your pupils in a discussion about robots that can detect objects:
- Do you know of any robots that can detect objects?
- Why is it useful for robots to be able to detect objects?
- What’s ultrasound, and how does an Ultrasonic Sensor work?
Building Tips
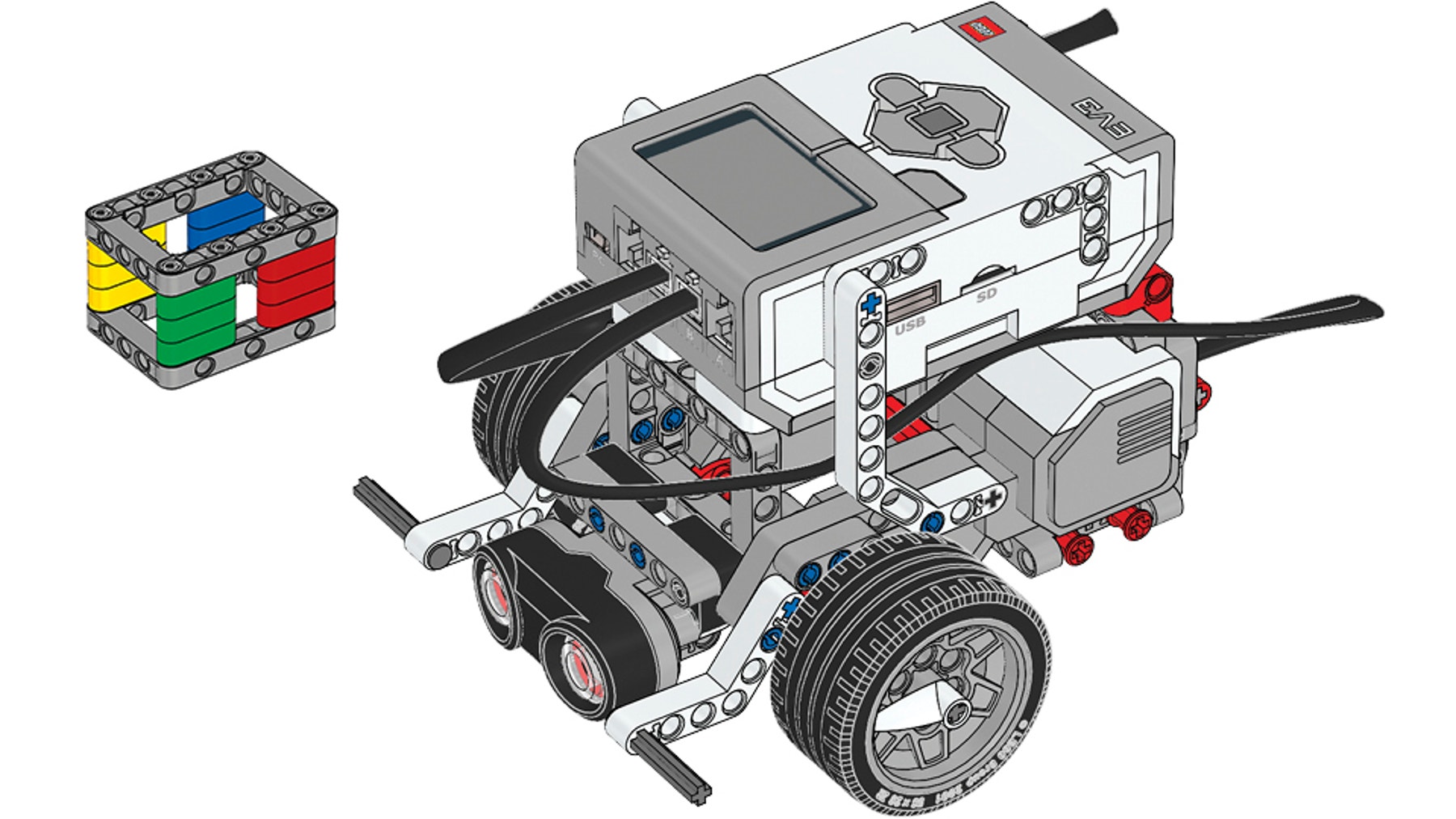
Building Instructions
Keep the Driving Base assembled after use, rather than taking it apart.
Coding Tips
Main Program

Possible Solution

Differentiation
Simplify this lesson by:
- Spending additional time explaining how to use the Ultrasonic Sensor
Take this lesson to the next level by:
- Challenging your pupils to program an autonomous robot that avoids obstacles
- Having your pupils use the Touch Sensor instead of the Ultrasonic Sensor to detect obstacles
Assessment Opportunities
Teacher Observation Checklist
Establish a scale that suits your needs, for example:
- Partially accomplished
- Fully accomplished
- Overachieved
Use the following success criteria to evaluate your pupils’ progress:
- The pupils are able to use the Ultrasonic Sensor to detect an object.
- The pupils are able to change the parameters of the Ultrasonic Sensor Blocks to detect different distances.
- The pupils are able to expand their programs to react dynamically to the detected distance.
Self-Assessment
Have each pupil choose the level that they feel best represents their performance.
- Bronze: I’ve used the Ultrasonic Sensor to stop at an object.
- Silver: I’ve used the Ultrasonic Sensor to detect the distance to an object.
- Gold: I’ve made one aspect of the program react dynamically to the distance to an object.
- Platinum: I’ve made several aspects of the program react dynamically to the distance to an object.
Language Arts Extension
To incorporate the development of language arts skills:
- Have your pupils prepare and deliver a presentation explaining how Ultrasonic Sensors work.
Note: This will require additional time.
Career Links
The pupils who enjoyed this lesson might be interested in exploring these career pathways:
- Manufacturing and Engineering (Machine Technology)
- Manufacturing and Engineering (Pre-Engineering)
Teacher Support
The pupils will:
- Use the Ultrasonic Sensor to detect and respond to an object
Computing at School Progression Pathways
Algorithms:
- Designs solutions (algorithms) that use repetition and two-way selection i.e. if, then and else.
- Uses logical reasoning to predict outputs, showing an awareness of inputs.
- Designs solutions by decomposing a problem and creates a sub-solution for each of these parts.
- Recognises that different solutions exist for the same problem.
- Recognises that different algorithms exist for the same problem.
Programming & Development:
- Creates programs that implement algorithms to achieve given goals.
- Uses post-tested loop e.g. ‘until’, and a sequence of selection statements in programs, including an if, then and else statement.
- Understands the difference between, and appropriately uses if and if, then and else statements. (AL)
- Uses a variable and relational operators within a loop to govern termination.
- Understands that programming bridges the gap between algorithmic solutions and computers.
- Uses a range of operators and expressions e.g. Boolean, and applies them in the context of program control.
Hardware & Processing:
- Knows that computers collect data from various input devices, including sensors and application software.
Information Technology:
- Makes appropriate improvements to solutions based on feedback received, and can comment on the success of the solution.
- Uses criteria to evaluate the quality of solutions, can identify improvements making some refinements to the solution, and future solutions.
- Designs criteria to critically evaluate the quality of solutions, uses the criteria to identify improvements and can make appropriate refinements to the solution.