Moves and Turns
Use the Driving Base to make precise and controlled movements.

Lesson plan
1. Prepare
- Read through the student material in the EV3 Classroom App.
- Collect some information about encoded motors and how they’re used in wheeled robots.
- You’ll need a measuring tape to measure how far the Driving Base drives.
- If you feel it’s needed, plan a lesson using the “getting started” material in the app. This will help familiarize your students with LEGO® MINDSTORMS® Education EV3.
- To complete this lesson, the students will have to have built the Driving Base model from the Get Moving “getting started” activity, which will take about 30 minutes.
2. Engage (10 Min.)
- Watch the unit video and use the ideas in the Ignite a Discussion section below to engage your students in a discussion related to this unit and lesson.
- Split your class into pairs.
3. Explore (15 Min.)
- Allow your students some time to use the programming stacks provided to explore the movement of the Driving Base.
- Ask them to describe the different turns they’ve observed.
- Let them rearrange the programming stacks to explore the different movements.
4. Explain (10 Min.)
- Facilitate a discussion about the importance of planning each step of a program.
- Explain what pseudocode is and how it can help your students as they plan their programs.
5. Elaborate (10 Min.)
- Have your students find a way to move their Driving Base for 84 cm/33 in.
- Don’t forget to leave some time for cleanup.
6. Evaluate
- Give feedback on each student’s performance.
- You can use the assessment rubrics provided to simplify the process.
Ignite a Discussion
An autonomous wheeled robot is a common type of mobile robot. Although they’re not yet common in homes, they’re used extensively in factories and warehouses around the world to automate tasks. The most basic task any wheeled robot should be able to do is to use its motors to make precise and controlled movements.
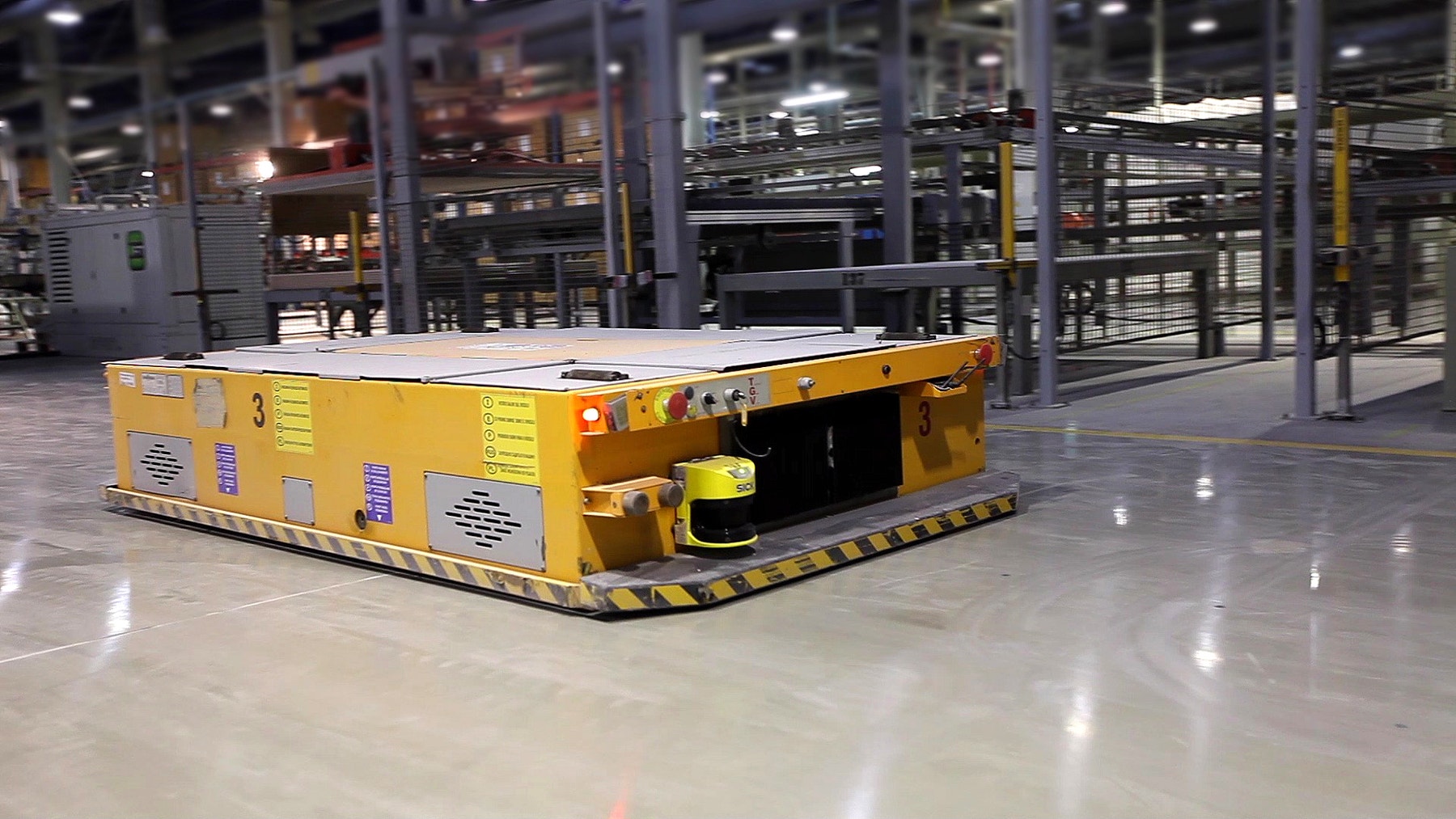

Watch the unit video and start a discussion about the role wheeled robots can play in automating tasks. Ask relevant questions, like:
- How could wheeled robots be configured and programmed to do specific tasks?
- What kinds of movements should they be able to make?
- How could they safely work together with human workers?
Building Tips
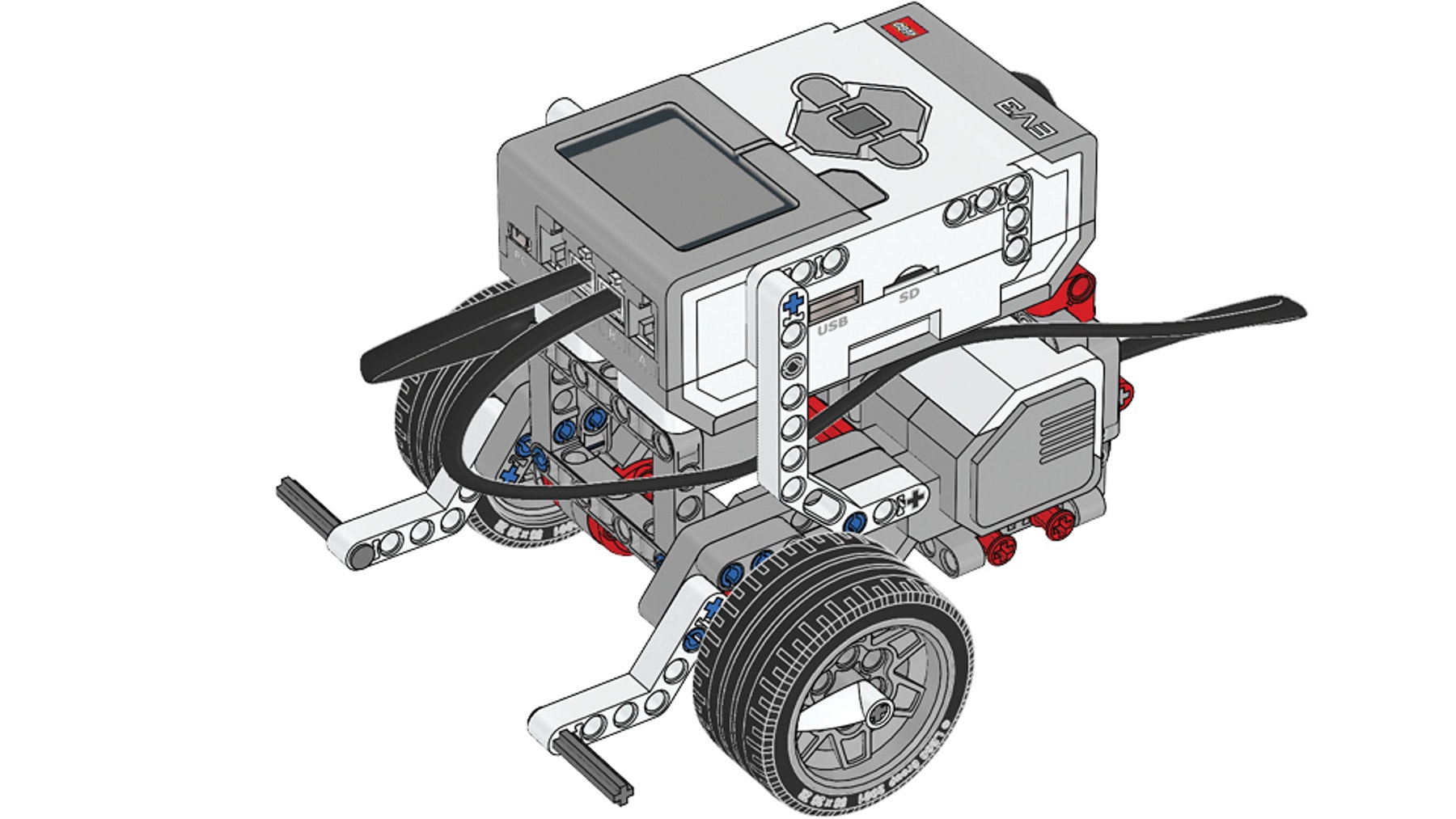
Building Instructions
Keep the Driving Base assembled after use, rather than taking it apart.
Coding Tips
Main Program

Possible Solution

Differentiation
Simplify this lesson by:
- Spending extra time explaining what’s being controlled by each parameter of the programming blocks
Take this lesson to the next level by:
- Having the students program the Driving Base to trace out a figure eight, the first letter of their name, or another letter or number
- Making an obstacle course that requires the use of different turning methods in order to complete it
Assessment Opportunities
Teacher Observation Checklist
Create a scale that matches your needs, for example:
- Partially accomplished
- Fully accomplished
- Overachieved
Use the following success criteria to evaluate your students’ progress:
- Students can select appropriate blocks for making controlled movements.
- Students can change the parameters of blocks in iterative ways.
- Students can stack appropriate Move Blocks together to create programs.
Self-Assessment
Have each student choose the level that they feel best represents their performance.
- Bronze: I’ve made the Driving Base move in one way.
- Silver: I’ve made the Driving Base move in different ways.
- Gold: I’ve created a program to move the Driving Base forward 84 cm/33 in.
- Platinum: I’ve used math to create a program to move the Driving Base forward exactly 84 cm/33 in.
Language Arts Extension
To integrate language arts skills development:
- Have your students look for the most precise way of traveling a distance of 2 meters by exploring these options:
- Move in seconds
- Move in degrees
- Move in rotations
- Ask them to create a document explaining in which situation(s) they’d use each option, and why.
Note: This will make for a longer lesson.
Career Links
Students who enjoyed this lesson might be interested in exploring these career pathways:
- Information Technology (Computer Programming)
- Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics (Engineering and Technology)
Teacher Support
Students will:
- Learn how to execute controlled movements (e.g., straight move, point turn, curved move) using a Driving Base
LEGO® MINDSTORMS® Education EV3 Core Set
EV3 Classroom App
A measuring tape
NGSS
MS-ETS1-4
Develop a model to generate data for iterative testing and modification of a proposed object, tool, or process such that an optimal design can be achieved.
CSTA
2-CS-01 6-8
Recommend improvements to the design of computing devices, based on an analysis of how users interact with the devices.
Common Core
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.B.4
Know the formulas for the area and circumference of a circle and use them to solve problems; give an informal derivation of the relationship between the circumference and area of a circle.
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.6.1
Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence.