LEGO® Education
SPIKE™ Prime
- LEGO® EducationSPIKE™ Prime
- Lessons by Subject
Supplementary Lessons – 21st Century Skills
Use these five hands-on lessons to coach and develop your students’ 21st century skills, including collaboration, creativity, communication, and critical thinking.
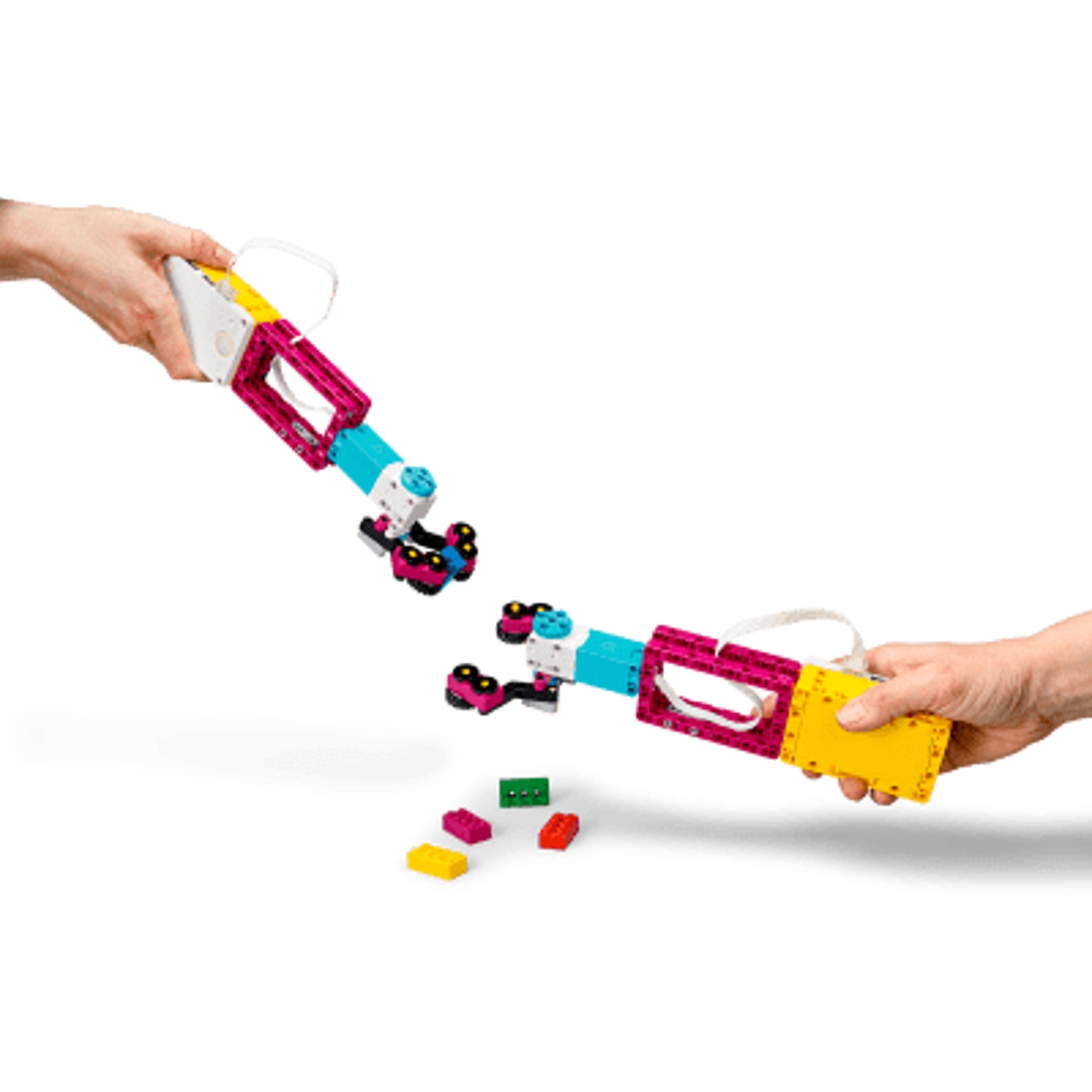

Pass the Brick

Ideas, the LEGO way!
Science & Engineering
These six LEGO Education SPIKE™ Prime lessons invite students to apply physical science concepts and the engineering design process through hands-on learning.

Hopper Race
Super Cleanup
Mathematics
These four SPIKE Prime lessons challenge students to apply mathematical concepts to authentic real-world contexts through hands-on learning.

Veggie Love
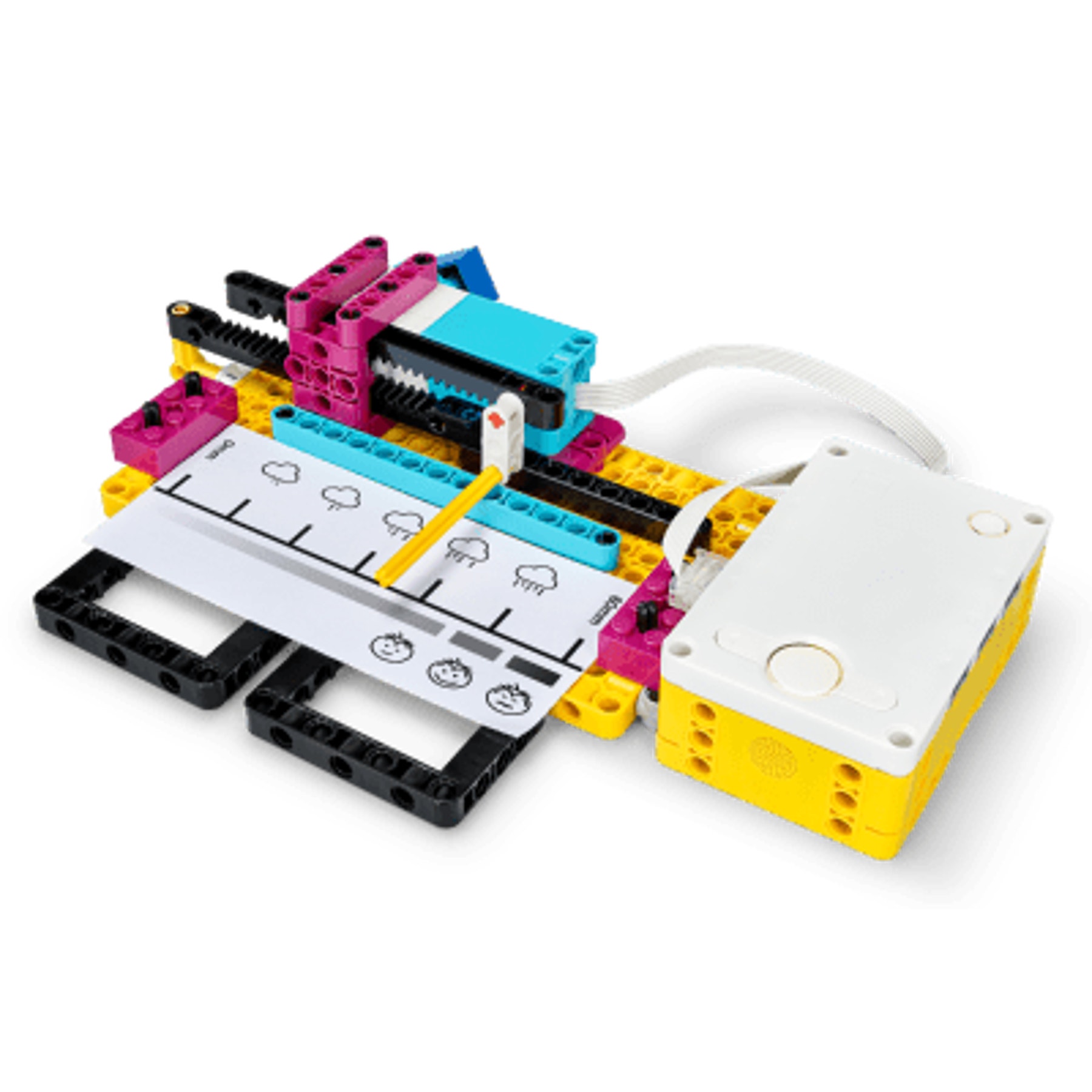
Rain or shine?
Data Science
These four hands-on SPIKE Prime lessons invite students to explore fundamental data science concepts, which help people make sense of information and apply it to decision-making. The lessons cover topics like practical applications of weather data and generating real-world data from our own movements—while building skills related to categorizing and labeling data, and discovering relationships between variables.
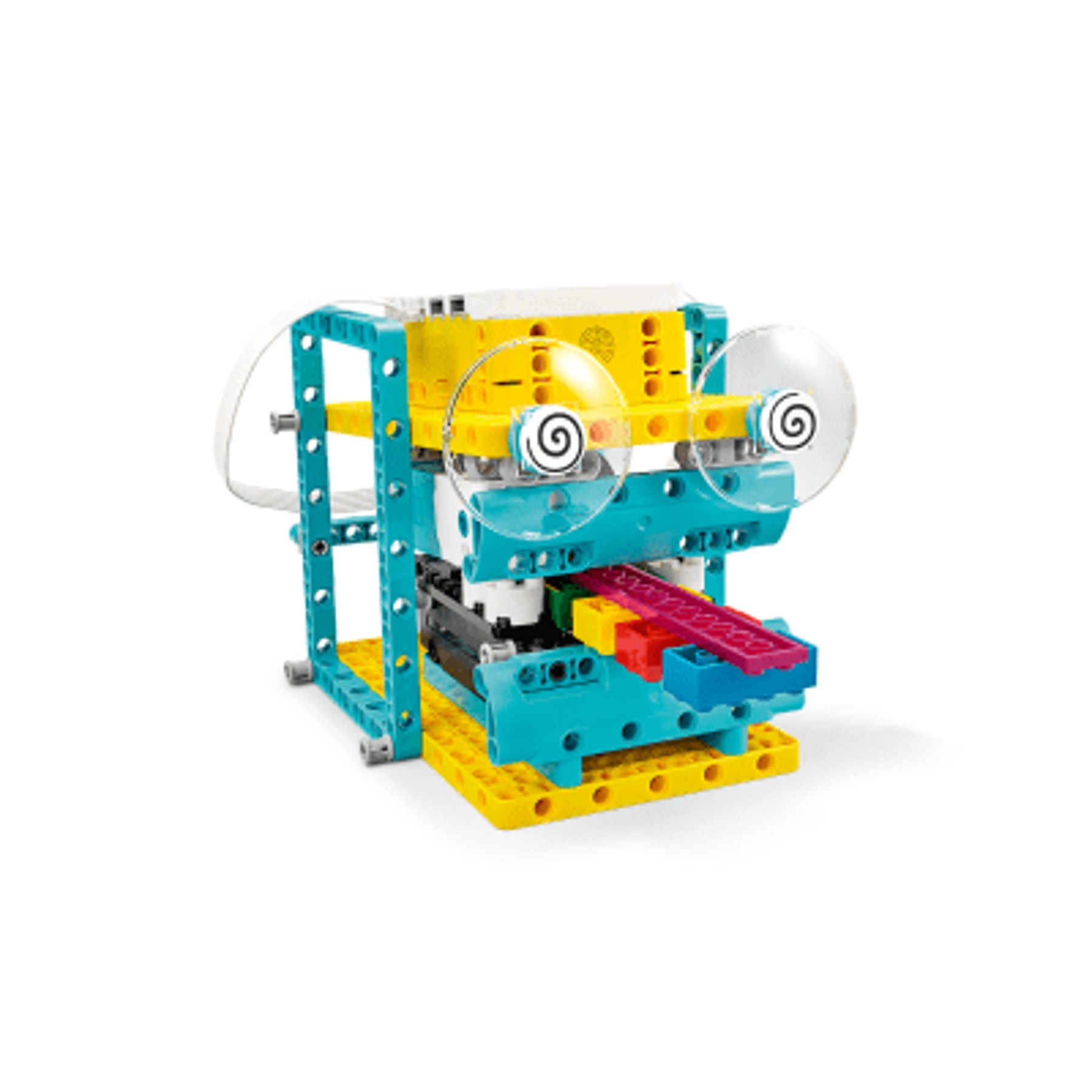

Brain Game
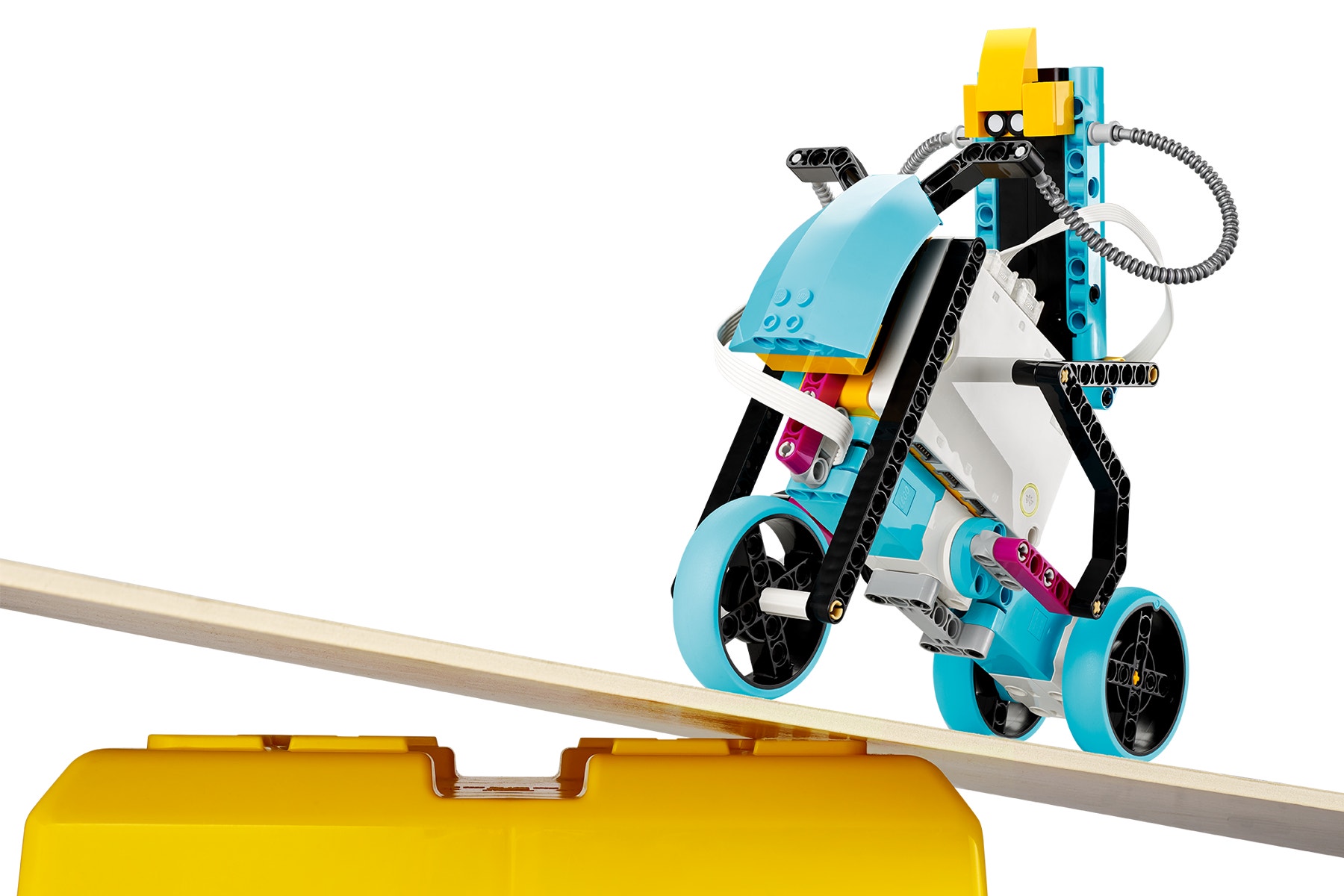

This Is Uphill
- Brain Game: In the math extension for this lesson, students collect and analyze data, learning fundamental skills for evaluating
information and making informed predictions about outcomes. - This is Uphill: Students collect and analyze data, learning fundamental skills for evaluating information and making informed
predictions about outcomes. - Stretch with Data: Students compare example data with data collected for validation, troubleshooting potential issues, and
supporting iteration. - Rain or Shine: Students use data from external sources to think critically about where data comes from and whether it’s valid and
reliable.
Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Both ML and AI belong to the field of computer science. AI reflects the idea that machines can execute tasks to mimic human-like intelligence. ML assumes that machines can learn and adapt through experience. AI applies ML to solve problems. These five hands-on SPIKE Prime lessons introduce students to some potential ML and AI applications, developing skills that will prepare them to learn how ML and AI work.

Brain Game
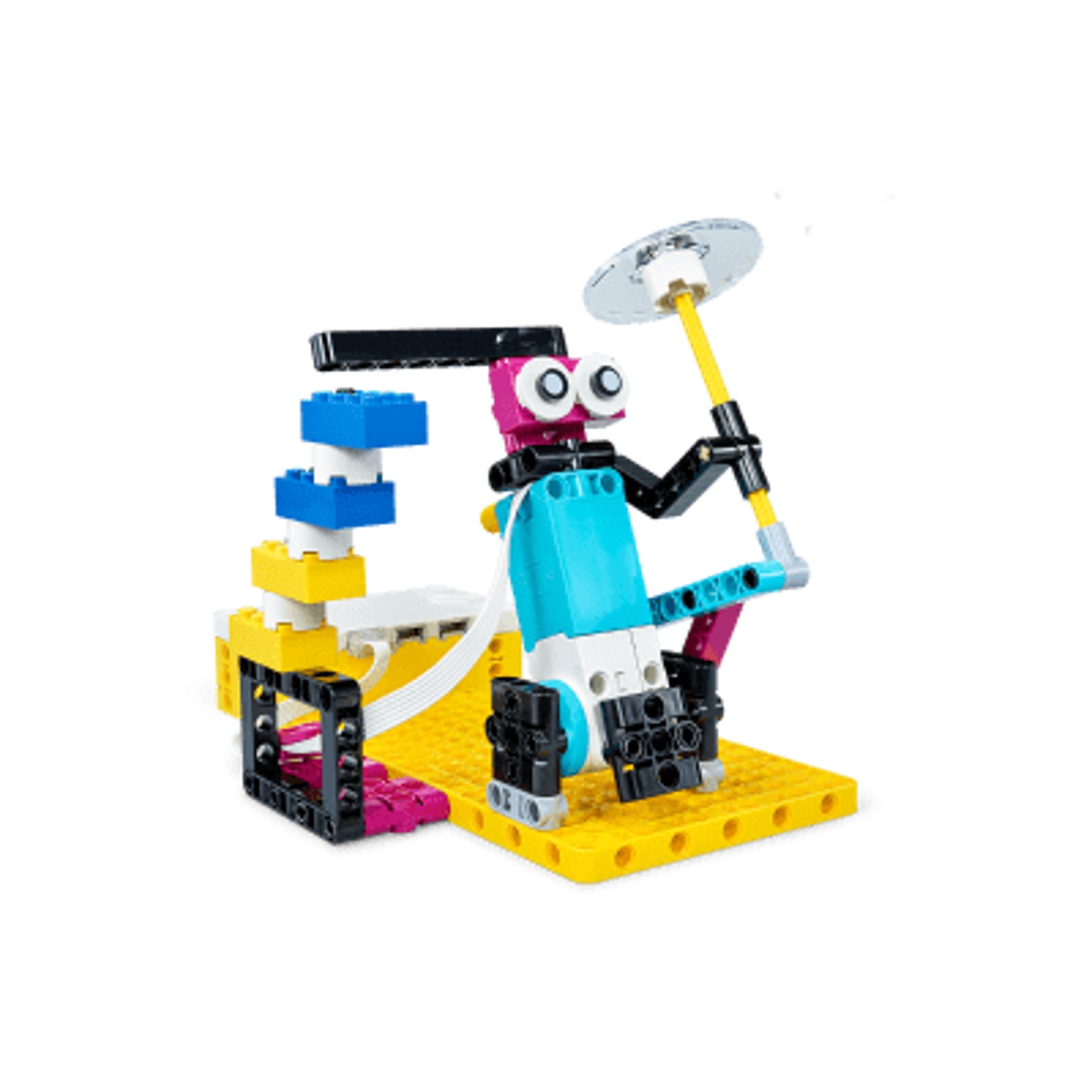

Wind Speed
- Brain Game: Students use a conditional statement (i.e., “if/then”) to
search for matches. This builds an understanding of how to provide
clear instructions via algorithms and program control structures,
which are essential to programming computers to eventually “think”
for themselves. - Wind Speed: Students learn about labels and classifications of data
ranges, preparing them for AI training called “supervised learning”
in which a computer program learns from labeled and classified
examples. - Watch Your Steps: Students collect sensor data via the built-in
accelerometer and use it to validate positioning, which enables them
to measure the position, orientation, and changes in an object’s
motion. Tracking and analyzing movements is fundamental to human
activity recognition in AI. - Repeat 5 Times: This lesson’s math extension teaches students about
linear functions and relationships. In ML, computers use linear
relationships to understand previous data behavior in order to
predict its future behavior. - Stretch with Data: Students learn about linear functions and
relationships. In ML, computers use linear relationships to
understand previous data behavior in order to predict its future
behavior.