Habitats
Sofie learned about the places giraffes live. She wonders about the other animals that live there. What about other places? Can you help her learn?

Prepare
(NOTE: This lesson contains a Part A and a Part B. Both are important to access the full learning of the standard. If time is limited, review both parts to choose elements that meet your students’ needs.)
In this lesson, the key learning is through observing the diversity of life in different habitats. Designing and building a model is a fun, hands-on way to show learning about that diversity in one habitat and observe classmates’ habitats to compare diversity in different habitats. Encourage students to build their ideas for a chosen habitat and the plants and animals that live in it. Reinforce that there is no single correct model.
Consider assigning one habitat to several groups (pairs). Each pair builds an animal from their assigned habitat, and each habitat group collaborates to combine their animals into a single habitat model. Finally, bring everyone together to compare all the plants and animals in the different habitats as a class. As needed, assign habitats to ensure diversity that supports comparison.
- Science Background - Habitats:
- A habitat is the natural home for a plant or animal. Every kind of habitat supports a variety of types of plants and animals.
- For animals, a habitat provides the food, water, climate conditions (temperature, moisture), and shelter that kind of animal needs to survive.
- For plants, a habitat provides the type of light and soil, and climate conditions (temperature, moisture) that kind of plant needs.
- Some common land habitats include savanna, forest, desert, mountain, grassland. Water habitats include oceans, rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, and swamps/wetlands.
- For young students, you may wish to start with very simple and familiar “habitats” like playgrounds, backyards, parks, or gardens, which students can personally observe.
- Build Prior Knowledge - Habitats: Using your core science materials, share information, images, and definitions to build prior knowledge.
- Review what students know about different habitats on Earth and the types of plants and animals that live in each one, including those near your school community. Students will learn more about the topic through this activity.
- Consider common plants and animals in habitats that the class has studied or that are near your school community, including simple ones like parks, ponds, or backyards.
- Key vocabulary: habitat, diversity
- Building and Programming Experience: Consider the suggestions in the Unit Plan. For this lesson, you may also want to
- Reinforce with the Color Sensor tutorial in the SPIKE App Start Menu
- Use the Event, Sensor (Color), and Sound Blocks sections of the Help>Icon Blocks menu in the SPIKE app to provide more support.
- Materials Locate age-appropriate books, materials, or online resources of different habitats. (search term: habitats + location, e.g. United States, your state, North America). Use sites from government agencies, science organizations, and educational institutions. Determine how you will share resources with students.
- To use the Extension activity, locate and provide learning materials about endangered animals or plants in the habitats represented in the class.
PART A (45 Minutes)
Engage
(Whole Class, 10 minutes)

Introduce the story’s main character(s) and the first challenge: Sofie learned about the places giraffes live. She wonders about the other animals that live there. What about other places? Can you help her learn?
THINK—Facilitate a brief discussion about the lesson topic(s) using the story picture if you wish.
- What is a habitat? (the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism; habitats are home to many different living things.)
- What are some types of habitats? What is in every animal’s habitat? (forests, grasslands, savannas, mountains, oceans, freshwater like a pond, stream, or lake; deserts, polar, and tundra; every habitat contains what the animals in it need to survive, including plants like trees, grasses, bushes, and flowering plants and animals like lizards, squirrels, fish, and clams.)
- Where do giraffes live? Describe their habitat. (Giraffes live mainly in savannas. Savannas are open spaces that have mostly grasses and other short plants, but savannas can have shrubs and trees too.)
- What are some other animals or plants that live in the same habitat as giraffes? (zebras, elephants, lions, etc.; grasses, trees, shrubs, etc.)
- Choose a habitat to explore and build. You’ll compare it with the habitats your classmates build.
Distribute a SPIKE™ Essential Set and device to each group.
Explore
(Small Groups, 25 minutes)
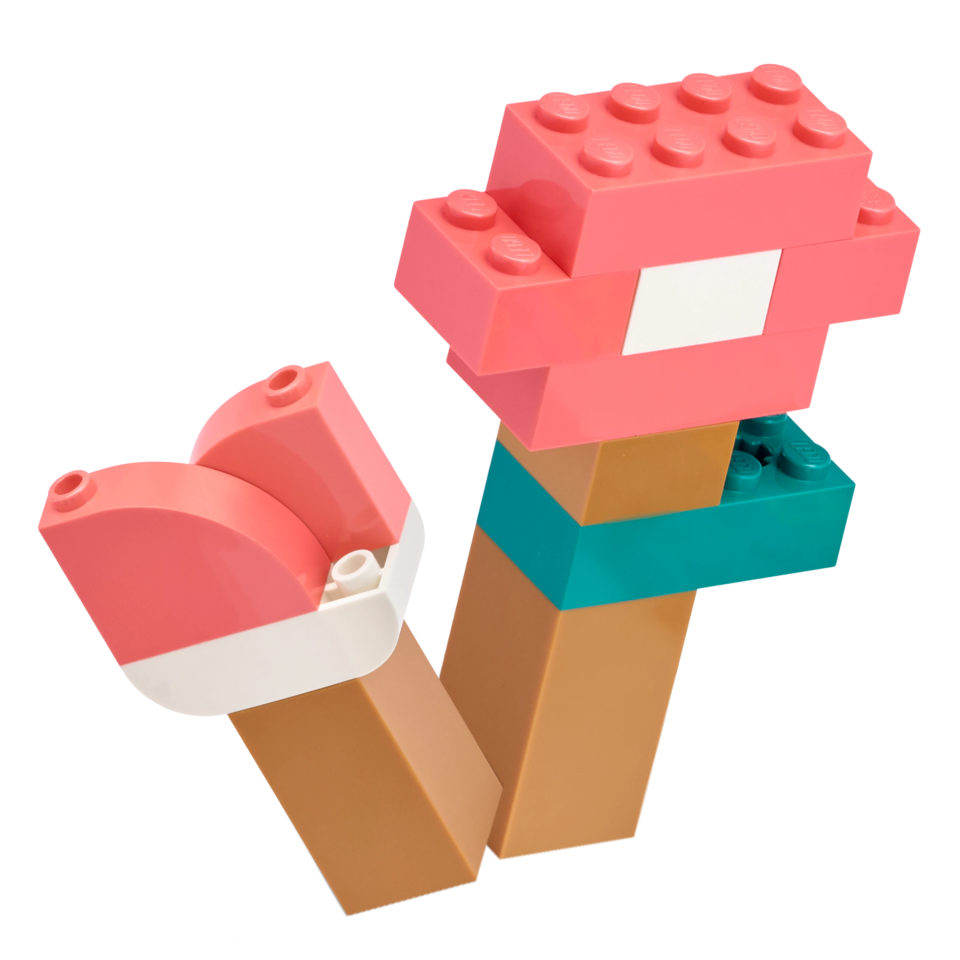
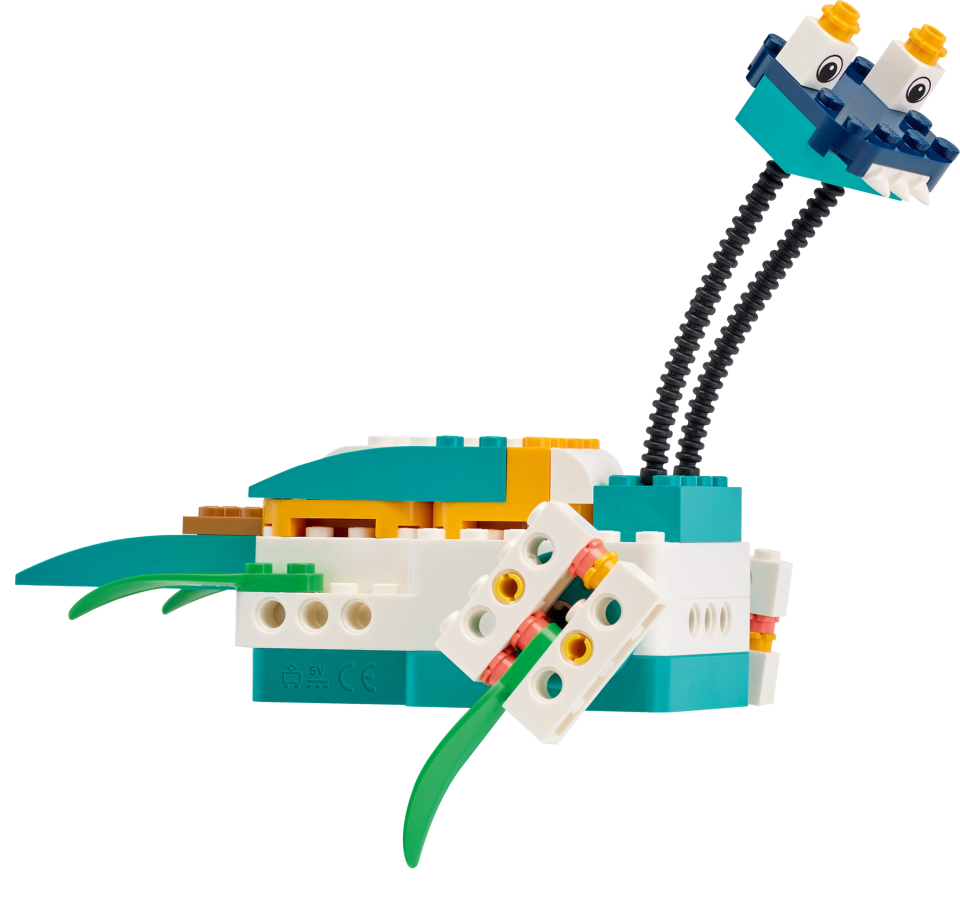
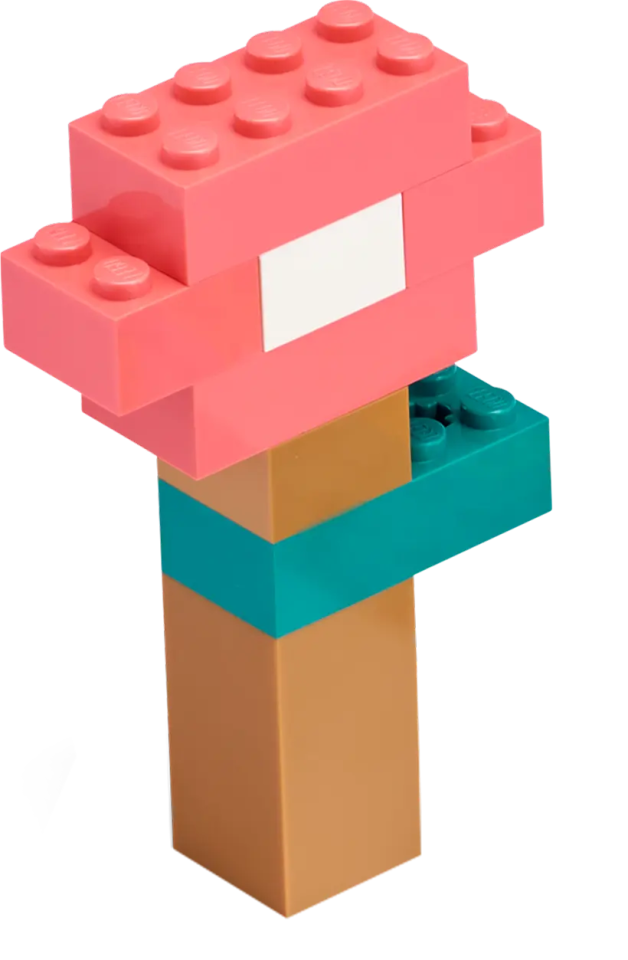
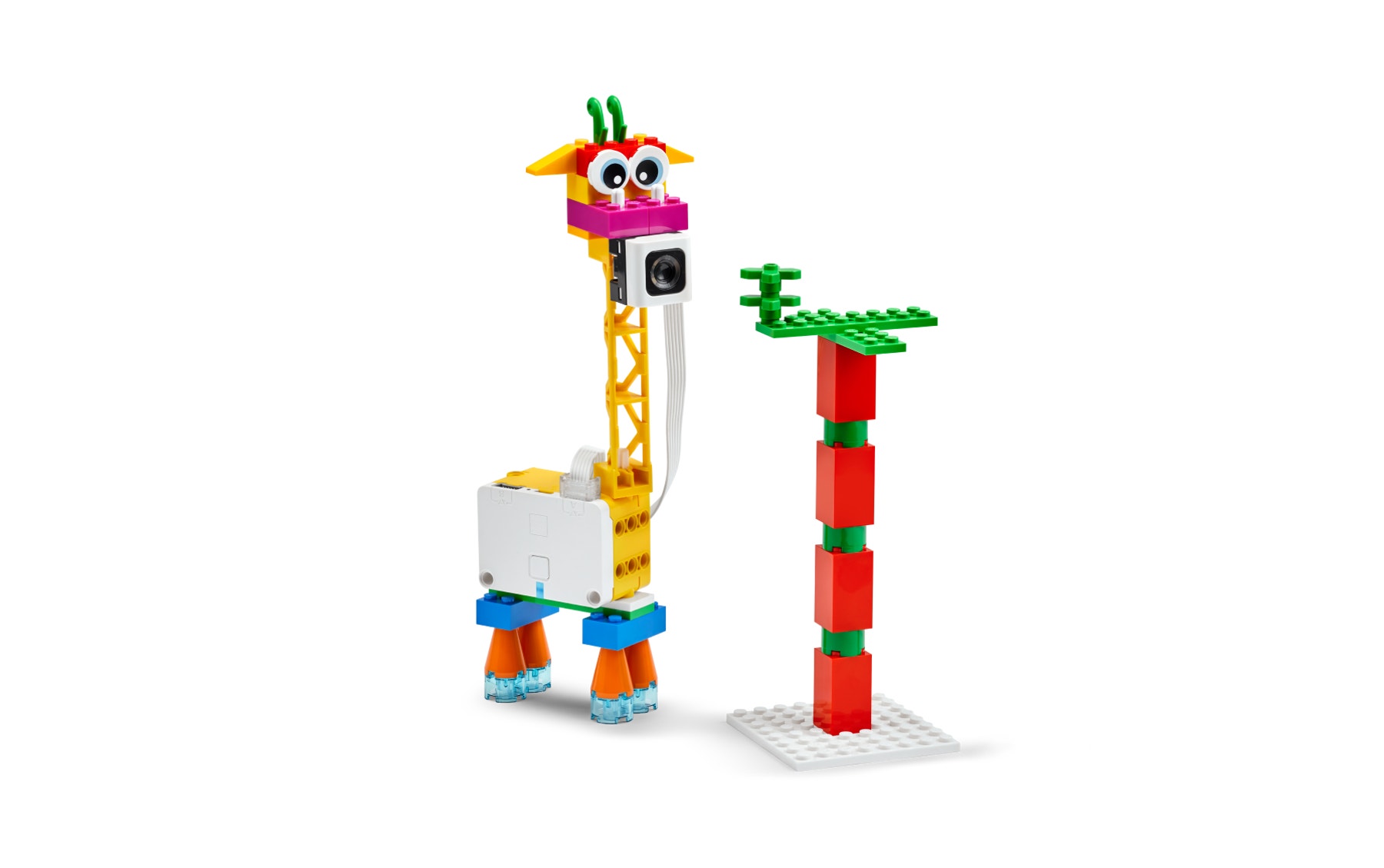
As students work, consider sharing the examples below as support for building or programming. Clarify that the images show ideas for one animal and habitat, but that students should build animals for their selected habitat.
Have students:
- Use the provided materials to learn more about a selected habitat.
- Use the base model to BUILD a habitat (assigned or self-selected), including its plants and animals.
- PROGRAM their model to show how animals live in the habitat.
Facilitate brainstorming on ways to combine the SPIKE™ Essential Set with different craft materials to create a habitat.
Clarify that the base model is for a giraffe and tree, but that students should build animals for their selected habitat.Halfway through work time, have students exchange ideas using a familiar classroom routine and then update their models with inspiration from sharing.
Example Ideas


Explain
(Whole Class, 10 minutes)
Gather students for sharing. Ask them to notice and record the different types of plants and animals that they observe in each habitat presented.
Have each group use their model to demonstrate and describe:
- What their habitat is like.
- What plants and animals live in the habitat.
After all groups have presented, have students share what they observed.
- What are the habitats built by other groups like?
- What plants and animals live in them?
- What is similar about the plants and animals in the various habitats? What is different?
If you wish to continue to Part B—Explain, have students keep their models intact.
PART B (45 minutes)
Explain
(Whole Class, 5 minutes)
- Repeat the steps from Part A - Explain to have additional groups demonstrate and explain their learning.
Elaborate
(Whole Class, 35 minutes)
(5 min)
- Organize a method for sharing, such as a Gallery Walk (viewers circulate to presenters) or Corners (assign each room corner a habitat and have students circulate to view multiple examples).
- Have students record their observations with sentence stems (“I saw animals like…. I saw plants like…”) in a T-chart (Plants; Animals) for each habitat type, by audio/video, or with annotated photos.
(25 min) Have your students iterate and test their models to complete the next challenge in the app:
- Compare the diversity of plants and animals in different habitats. Use what you observed.
- Program one of the group’s plants or animals to show a way the habitat is the same as or different from other habitats.
(5 min) Invite students to share knowledge, ideas, or skills that:
- Helped them complete the challenge.
- They learned while building.
Have students clean up the sets and work areas.
Evaluate
(Whole Class, 5 minutes)
- Ask guiding questions to elicit students’ thinking and their decisions while ideating, building, and programming.
Observation Checklist
Review the learning objectives (Teacher Support box).
Share specific student responses and behaviors at different levels of mastery.
Use the checklist to observe students’ progress:
- Their written, audio, or visual record includes observations of the plants and animals in the various habitats discussed.
- They use observations to describe common plants and animals in different habitats.
- They accurately note what is the same or different among the plants and animals within a habitat and across different habitats.
- They build a model of a habitat that has appropriate plants and animals.
Self-Assessment
Have each student choose the brick that they feel best represents their performance。
- Blue brick: I think I can follow instructions to create a program.
- Yellow brick: I can follow instructions to create a program.
- Green brick: I can follow instructions to create a program, and I can help a friend do it too.
Peer-Feedback
In their small groups, have your students discuss their experiences working together.
Encourage them to use statements like these:
- I liked it when you…
- I’d like to hear more about how you…
Differentiation
Simplify this lesson by:
- Having students build a model with one specific animal or plant living in a habitat, specifying a habitat the class has studied, or defining a habitat with a previously observed local habitat such as a nearby pond or park.
Increase the difficulty by:
- Extending the Elaborate challenge to have student groups program two of their animals to interact in some way or by inviting multiple groups to build adjacent habitats that animals may go between.
Extension
- Provide learning materials about endangered animals or plants in the habitats represented in the class. Have students choose an example to explore. Ask them to write or speak, asking for change in the form of 1) a postcard from the animal, 2) a written or recorded public service announcement (PSA), or 3) a letter to the school newspaper.
If facilitated, this will extend beyond the 45-minute lesson.
Language Arts: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.2.1
Teacher Support
Students will:
- Record observations of the types of plants and animals that live in different habitats.
- Compare the diversity of life in different habitats.
- Build a model that shows important features of a habitat, including the plants and animals that live there.
(one for every two students)
- LEGO® Education SPIKE™ Essential Set
- Device with the LEGO Education SPIKE App installed
- See Prepare - Materials.
Meet the team: Minifigure Bios
- NGSS 2-LS4-1: Make observations of plants and animals to compare the diversity of life in different habitats.
- NGSS K–2-ETSI-1
- CSTA 1A-AP-10
- ISTE 1.4c
- CCSS.ELA.LITERACY.SL.2.1
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.2.OA.B.2
Language Arts Extension
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.2.1