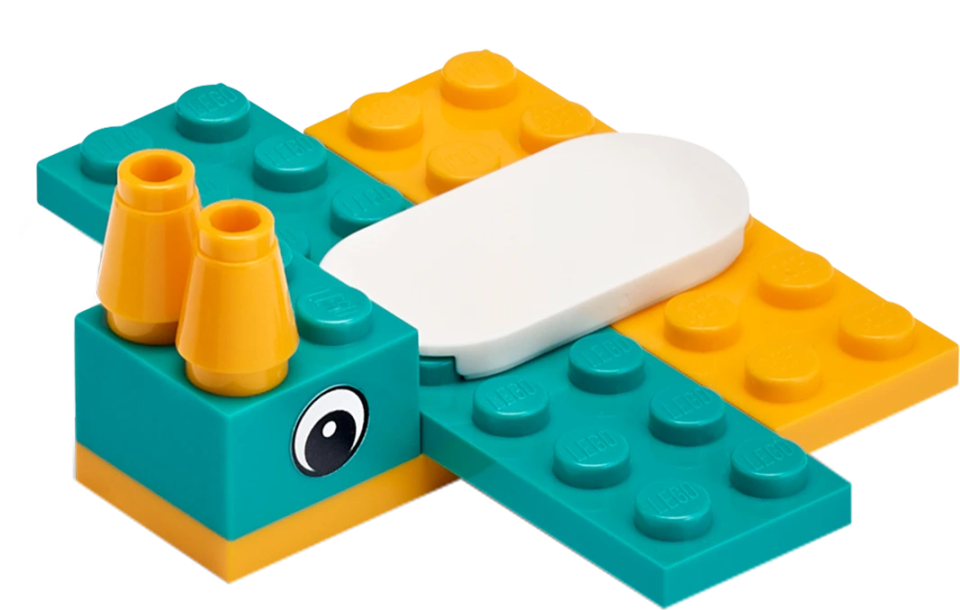
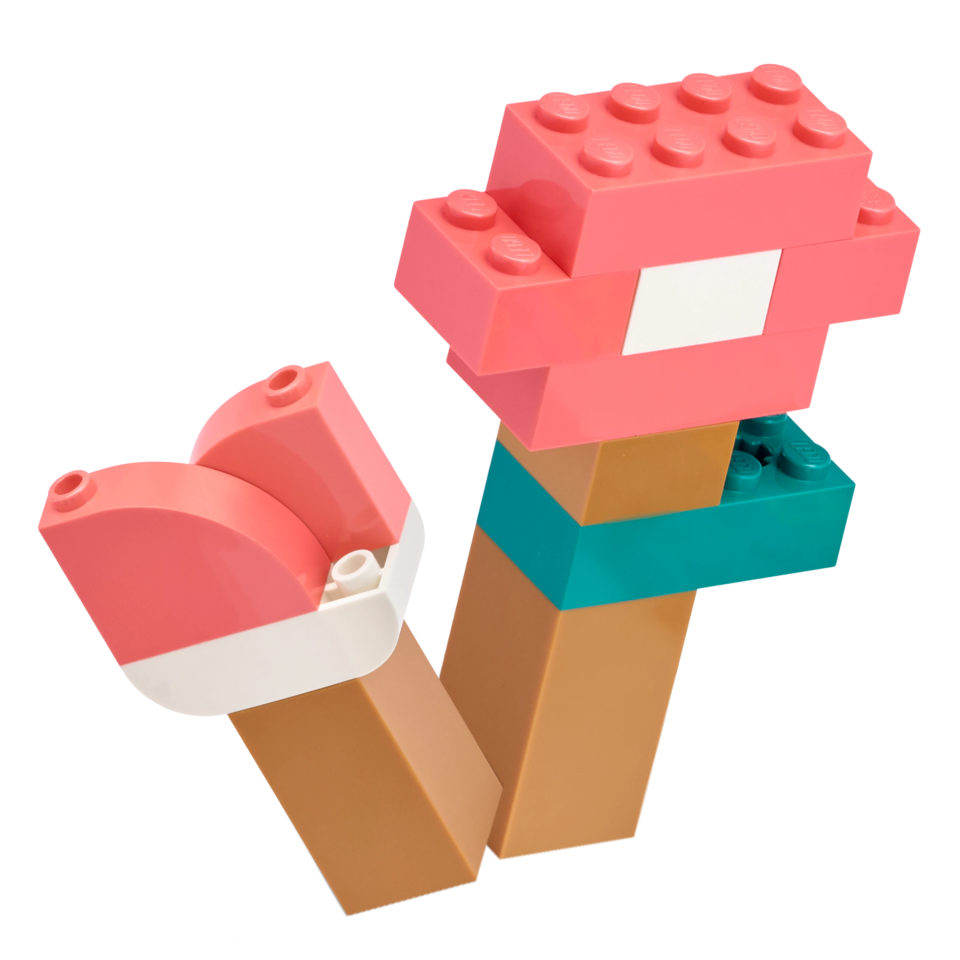
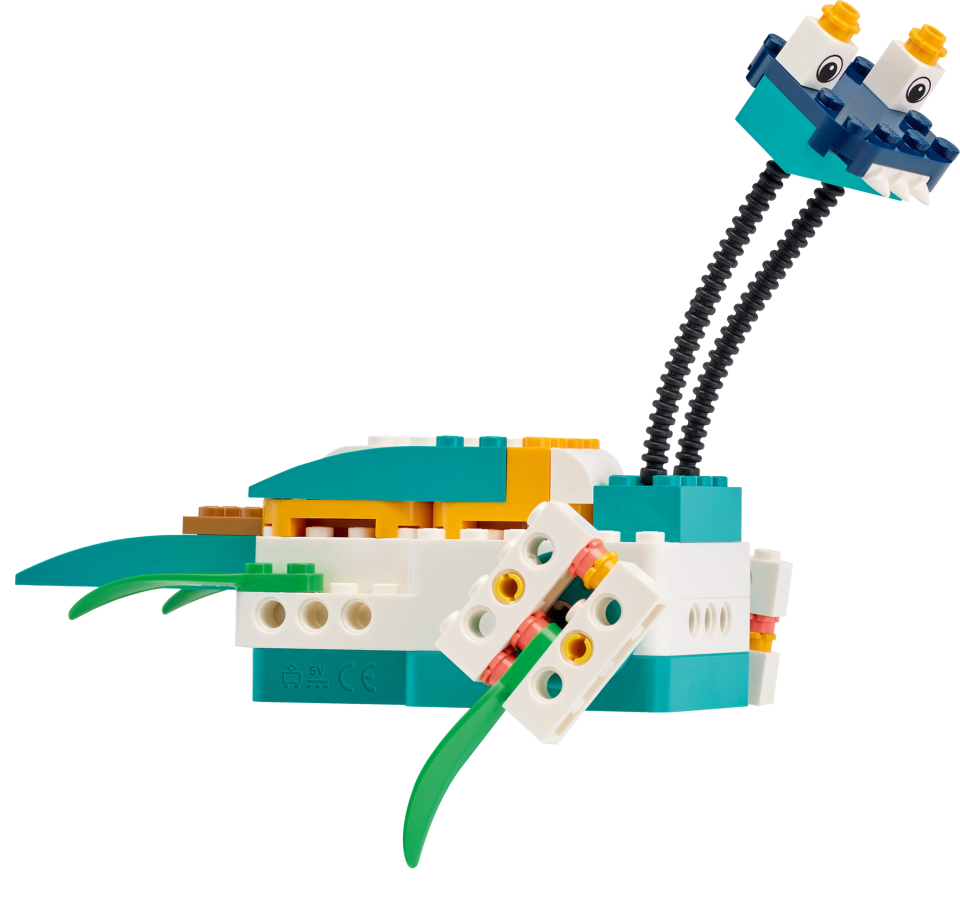
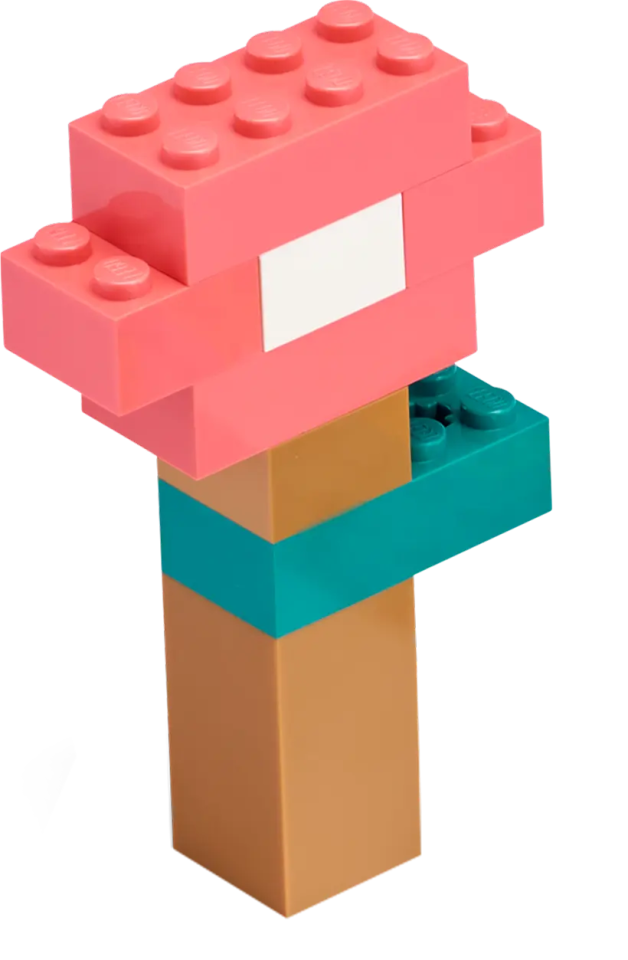
Launch the Satellite
Design, build, and program a robot that can place the Satellite inside the marked area on the Challenge Mat.

Lesson Plan
1. Prepare
- Read through the student material in the EV3 Classroom App.
- Collect some information about communication satellites and how they’re used in deep space communication.
- If you feel it’s needed, plan a few lessons to go through the Robot Trainer unit in the app. This will help familiarize your students with LEGO® MINDSTORMS® Education EV3.
- To complete this lesson, your students will have to have built the eight Space Challenge models and set up the Challenge Mat.
- If you don’t have double-block class time, plan to run this lesson over multiple sessions.
Part A
2. Engage (10 Min.)
- Use the ideas in the Ignite a Discussion section below to engage your students in a discussion related to this mission.
- Explain the objective, rules, and achievement badges for this mission.
- Split your class into teams.
3. Explore (25 Min.)
- Have your students brainstorm ideas for solving this mission.
- Encourage them to create multiple prototypes, exploring both building and programming.
- Allow the teams some time to work independently on building and testing their solutions.
4. Explain (10 Min.)
- Facilitate a discussion about the key functionalities the robot must have in order to navigate to the marked area and place the Satellite inside it.
Part B
5. Elaborate (45 Min.)
- Have each team practice lining up their robot and sending it on the mission to launch the Satellite.
- Let them continue working on their robots until they’re ready for a judged attempt.
- Don’t forget to leave some time for cleanup.
6. Evaluate
- Award achievement badges based on how well each team solved the mission.
- Evaluate the creativity of each team’s solution and how well their team worked together.
- You can use the assessment rubrics provided to simplify the process.
Ignite a Discussion
A communication satellite relays and amplifies radio waves from an Earth-centered orbit to different locations on Earth. Radio waves travel in a straight line, so there needs to be a line-of-sight between the sender and receiver. Satellites in orbit are better suited to maintaining a line-of-sight with Mars than Earth-based antennae. They’re also relatively unaffected by electromagnetic interference or atmospheric disturbances.

Use these questions to engage your students in a discussion about how communication satellites can be used in deep space communication:
- What’s a communication satellite?
- How are satellites used in deep space communication?
Mission Goal
The robot navigates to the marked area and places the satellite inside it.
Here’s an example mission solution that completes this mission:
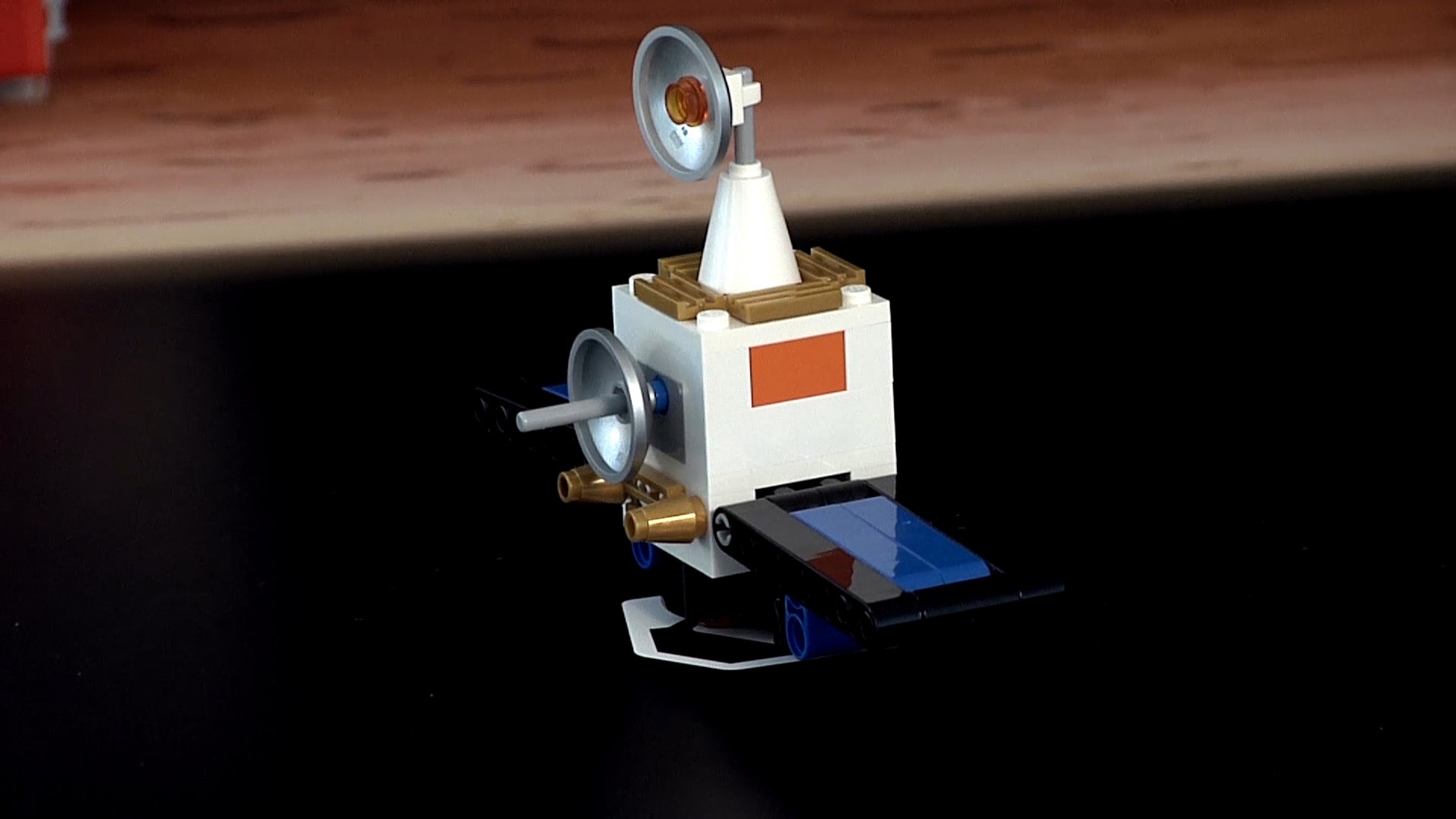
Mission Rules
There are five rules that apply to all of the Space Challenge missions. Make sure your students know all of them before they start:
- Your robot must always start the mission from the base area.
- Your robot must leave the base area before carrying out the mission.
- A “successful robot return” occurs when any part of the robot crosses over any part of the base area line.
- You’re not allowed to touch your robot while it’s outside of the base area.
- If you touch your robot while it’s completely outside of the base area and it’s holding an object, the object must be returned to its original position and you must begin the mission again.
Mission Achievement Badges
There are four levels of achievement badges. Explain that each team will be awarded an achievement badge based on how well they accomplish the mission. Refer to the Assessment Opportunities section below for a description of the achievement badges for this mission.
Building Tips
Open-Ended Solutions
This project is designed so that every team can have a unique solution. Use these questions to help teams brainstorm ideas for solving this mission:
- What are some ways the robot could navigate to the marked area?
- Which type of motorized mechanism can be used to place the Satellite carefully and accurately in the marked area?

Example Mission Solution
The example mission solution is comprised of the following solution extensions:

Execute the Mission
Place the example solution model in starting position “2” on the Challenge Mat, place the Satellite on the Satellite Module, and execute the mission.

Mission Troubleshooting
Rather than using the Color Sensor to find the marked area on the Challenge Mat, measure the angle and distance to navigate a carefully planned trajectory instead.
Coding Tips
Solution Program

Important
This program is unique to the example solution model described above. Due to variations in friction, battery level, lighting conditions, and the condition of the LEGO® components, it’s likely that you’ll have to make adjustments to the program. Before doing this, however, try making small adjustments to the robot’s starting position in the base area.
Differentiation
Simplify this lesson by:
- Working side-by-side with your students to help them figure out how to navigate to the marked area
- Having your students complete the Moves and Turns lesson in the Robot Trainer unit before attempting this mission
- Encouraging peer-to-peer learning and coaching
Take this lesson to the next level by:
- Limiting the amount of time the students have to solve the mission
- Adding design constraints by limiting the number of LEGO® elements available or assigning a “price” to each type of LEGO element and a maximum “cost” per robot
Assessment Opportunities
Teacher Observation Checklist
Create a scale that matches your needs, for example:
- Partially accomplished
- Fully accomplished
- Overachieved
Use the following success criteria to evaluate your students’ progress:
- Students designed a robot that meets the requirements of the mission.
- Students came up with creative solutions and considered multiple solutions.
- Students worked together as a team to complete the mission.
Achievement Badges
Award an achievement badge based on how well the team solved the challenge mission.
- Bronze: No part of the Satellite rests inside the marked area.
- Silver: Parts of the Satellite rest outside the marked area.
- Gold: Every part of the Satellite rests inside the marked area.
- Platinum: Every part of the Satellite rests inside the marked area. The team also went beyond the mission requirements by adding features to their design.

Self-Assessment
Have each student choose the achievement badge that they feel best represents their performance.
- Bronze: We did the best we could under difficult circumstances.
- Silver: We had a few accidents along the way but we still battled on to the end of the mission.
- Gold: We’ve accomplished the mission with excellent results.
- Platinum: We’ve not only completed the mission but also added original and effective features to our design.
Language Arts Extension
To integrate language arts skills development, have your students:
- Create a presentation or a video highlighting their robot’s features and performance
- Create a presentation explaining some important features of their program
Note: This will make for a longer lesson.
Career Links
Students who enjoyed this lesson might be interested in exploring these career pathways:
- Information Technology (Computer Programming)
- Manufacturing and Engineering (Pre-Engineering)
- Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics (Engineering and Technology)
Apoyo docente
Students will:
- Demonstrate their skills in solving a mission
NGSS
MS-ETS1-4
Develop a model to generate data for iterative testing and modification of a proposed object, tool, or process such that an optimal design can be achieved.
Common Core
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.SL.7.1
Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 7 topics, texts, and issues, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly.
ISTE
4B
Students select and use digital tools to plan and manage a design process that considers design constraints and calculated risks.
7C
Students contribute constructively to project teams, assuming various roles and responsibilities to work effectively toward a common goal.
Material para los estudiantes
HOJA DE TRABAJO PARA EL ALUMNO
Descargar, consultar o repartir como una página HTML online o como PDF para imprimir.